During our summer hiatus, the third interstellar object was discovered, 3I/ATLAS. Now we have three different interstellar interlopers to compare and contrast.


During our summer hiatus, the third interstellar object was discovered, 3I/ATLAS. Now we have three different interstellar interlopers to compare and contrast.

Normally we try to end the season on a high note. But here’s the unfolding news: NASA’s new budget is here, and it’s 25% smaller.
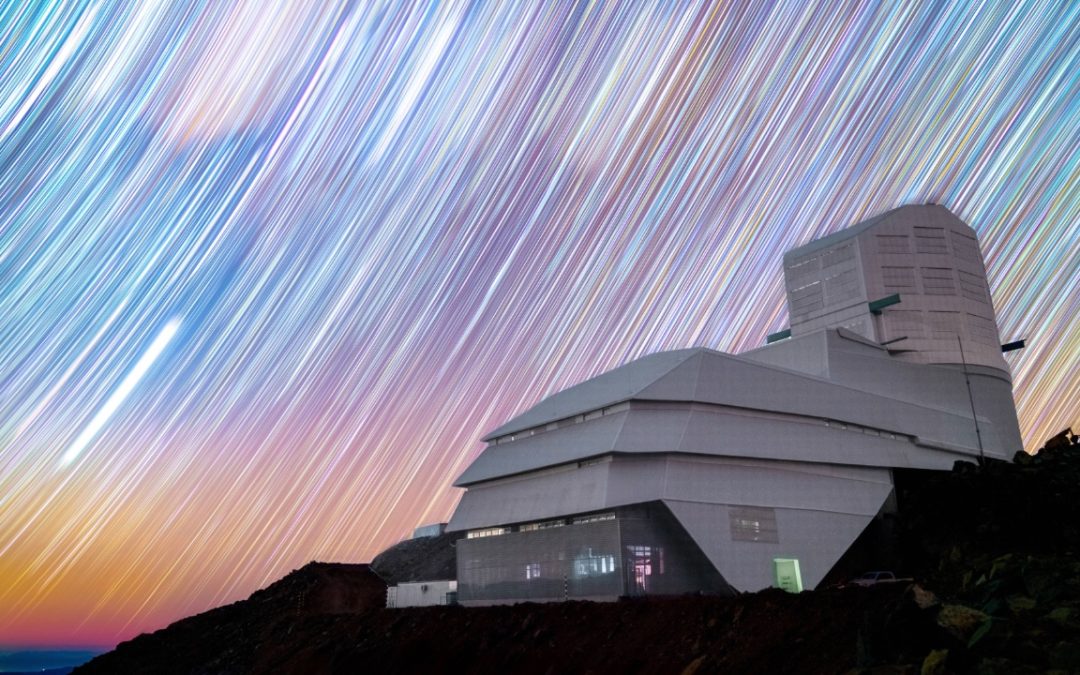

The time has come. The mighty Vera Rubin Observatory has finally come on line and delivered its “first light” images

It’s almost time for our annual summer hiatus, but before we go, we wanted to direct you towards all the fun and space stuff we’ll be enjoying this summer. We’ve got meteor showers, planets, rocket launches, TV shows, movies! Here’s what’s good. In a couple of weeks,…
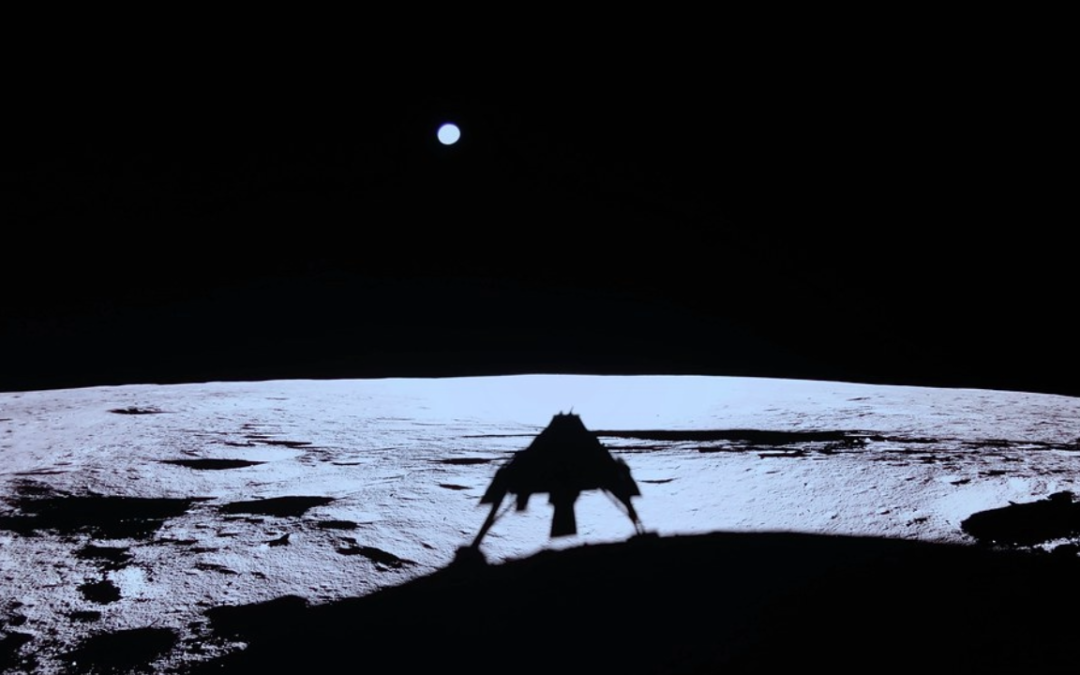

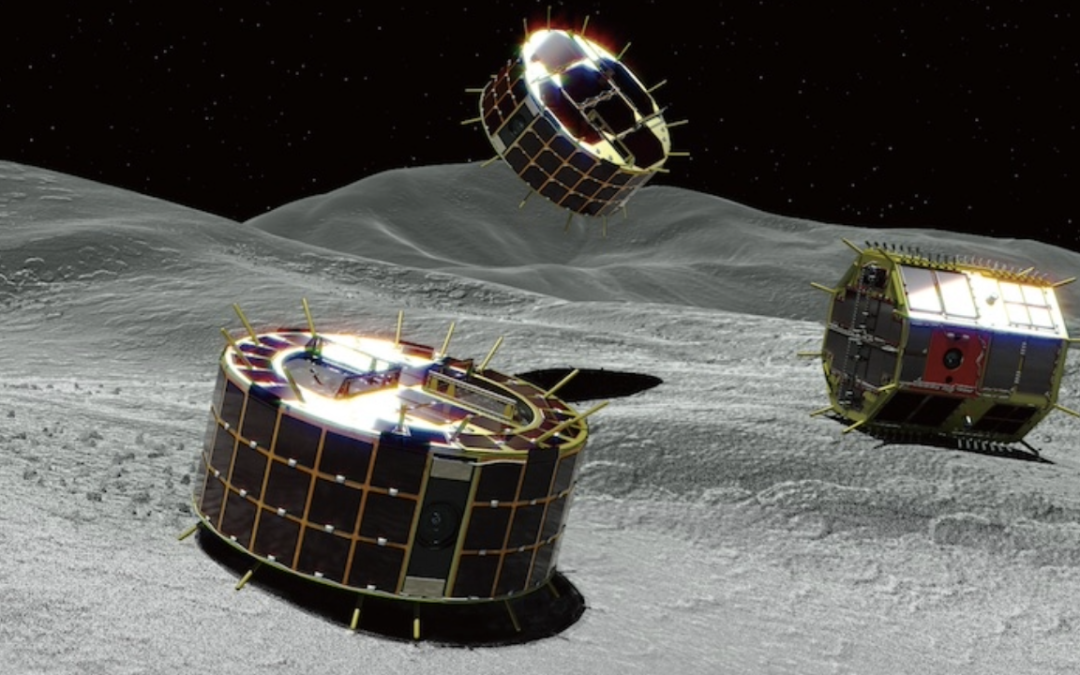
Humanity has turned its focus back to the Moon, sending a fleet of spacecraft to the lunar surface. Some are run by the government, but there’s a whole new group of commercial landers bearing instruments to the lunar surface. Is this the future of lunar exploration?…

Astronomy Cast dive into the wild world of non-roving rovers. The future of exploration isn’t just rolling… it’s hopping, flying, crawling, and swimming!
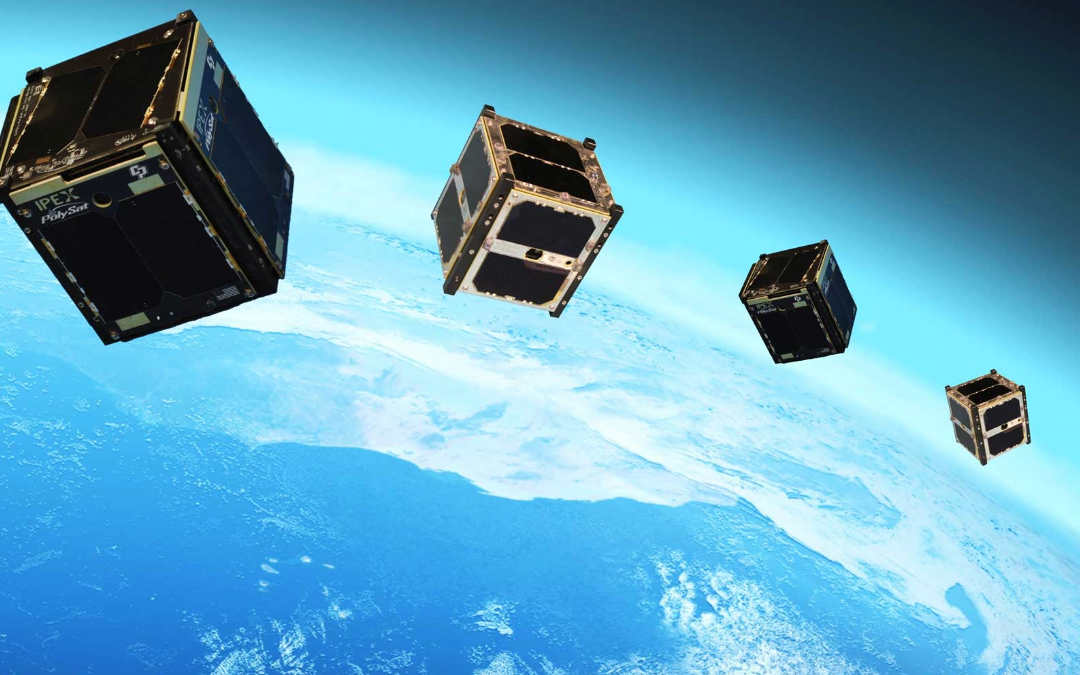

Computers are getting smaller, faster and more capable, which has enabled an entirely mew class of satellites: CubeSats.
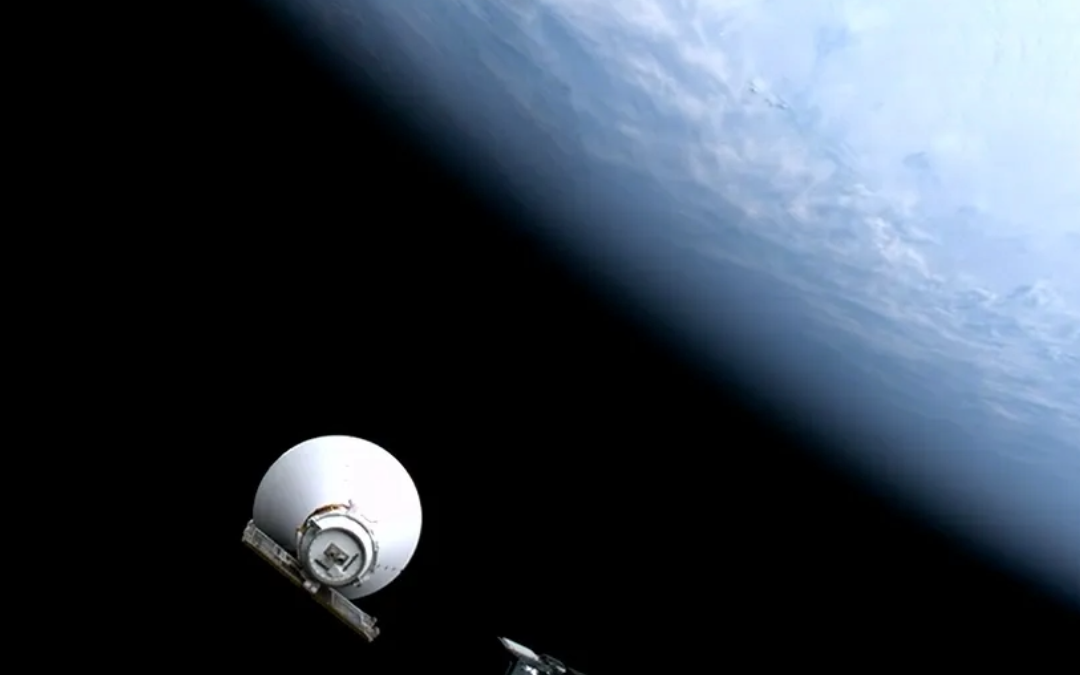

NASA’s newly launched SphereX mission is up & operational and has completed its initial checkout and “first light”. Everything looks good! And now it’s starting its science operations.

There are stellar-mass & supermassive black holes. But very little evidence of anything in between. Where are all the intermediate-mass black holes?

It’s in the news and people are claiming aliens… but is it aliens? Let’s see what the data actually says.

It seems like everyone just wants to explore the Moon’s South Pole. What makes this region so special and what are the special challenges that explorers will face. Learn here!

We are on the verge of sending humans back to the Moon. At the same time others prefer we focus our exploration on Mars. It’s a tough choice.

Even empty space isn’t empty. It’s filled with quantum fluctuations of spacetime itself. Which can be measured with Casimir Effect experiment
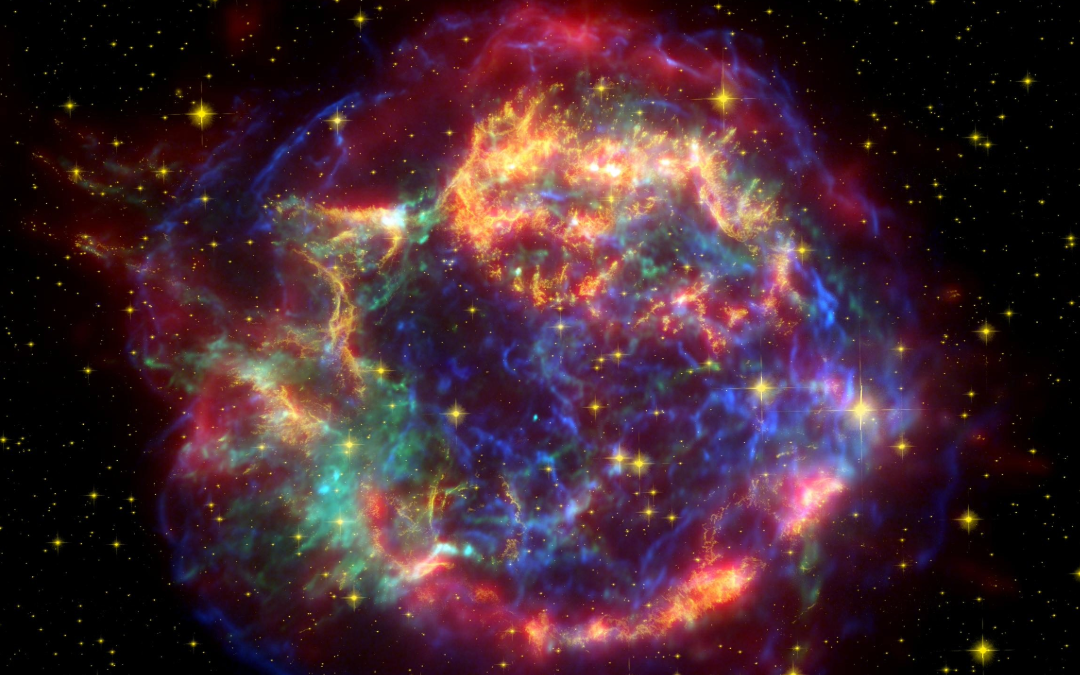
If we can accurately detect neutrinos being emitted during supernova, we might be able to get on target before the light show even starts.
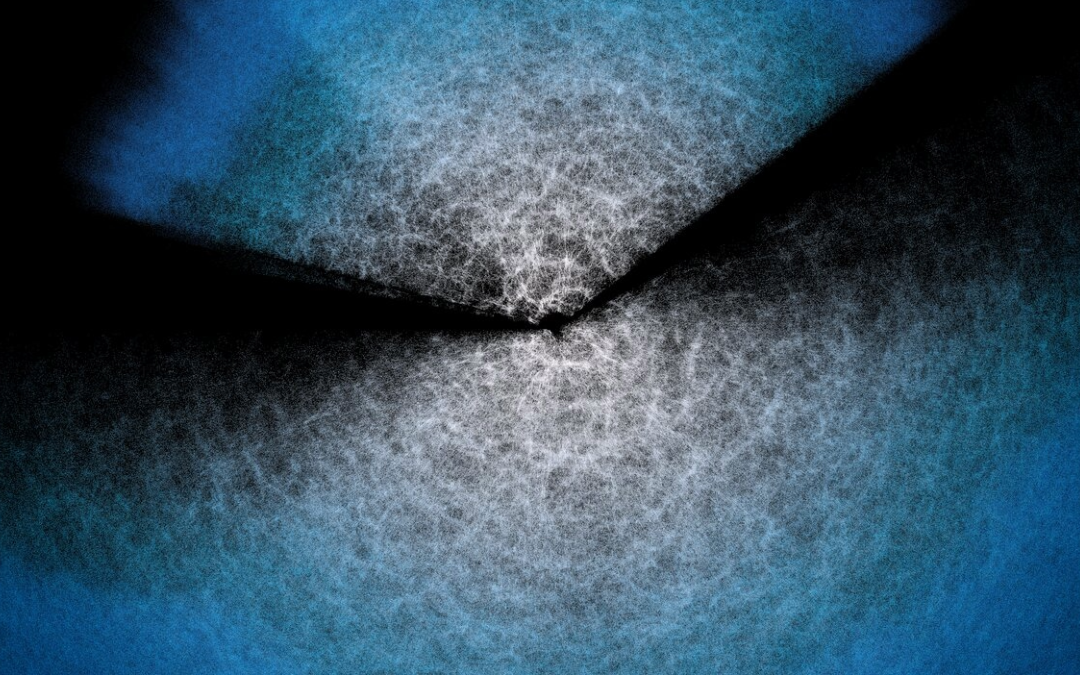
We thought Dark Energy was constant, but new results from DESI say maybe not, and if it wasn’t the Hubble Tension would be easier to solve.
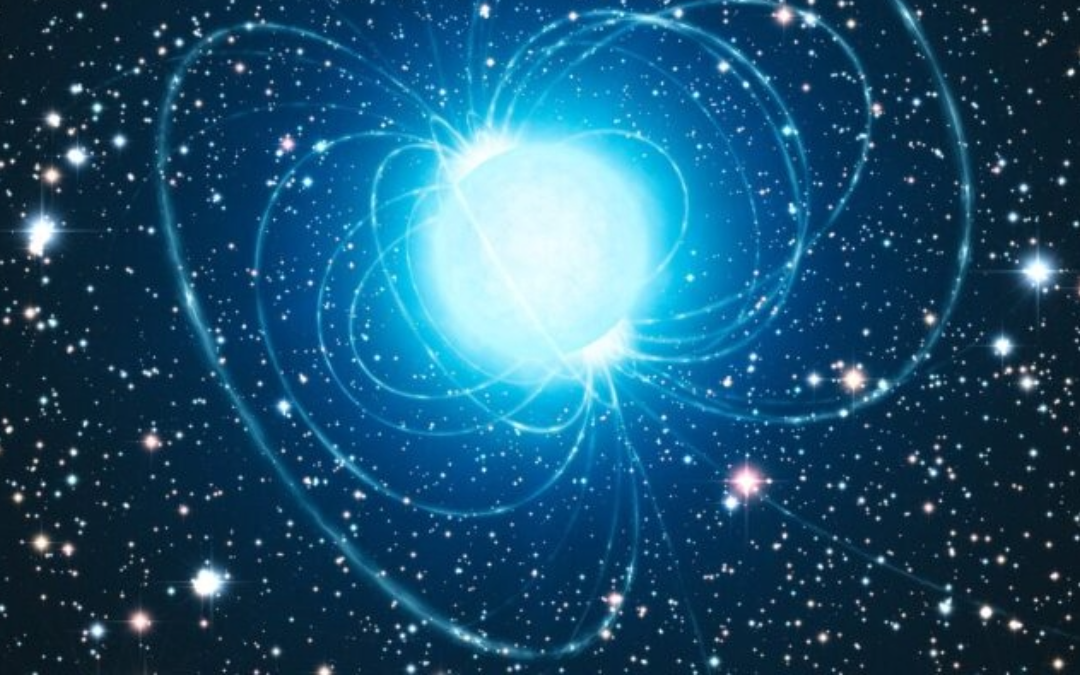

Fast Radio Bursts the briefest of moments, some dead stars can flash brighter than their entire galaxy (in Radio light) and then live to do it again and again. It’s time for an update on fast radio bursts, a phenomenon we’ve only known about for a few decades.
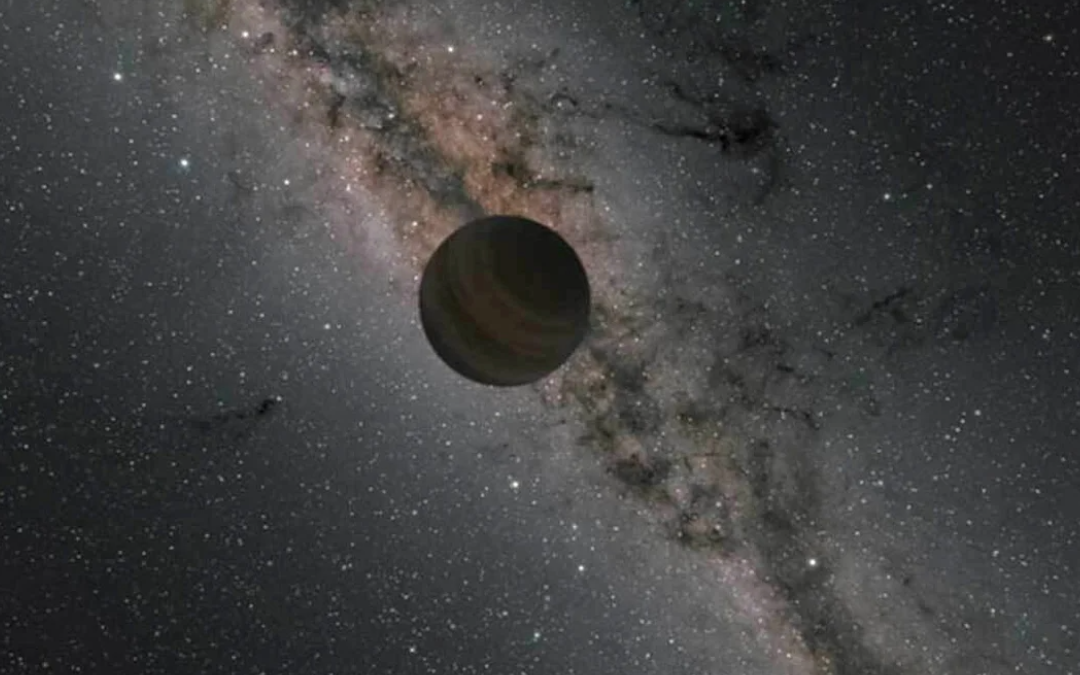

Most planets orbit stars. That’s the rule, right? Sometimes planets just go rogue. Let’s learn about planets living free from stars.
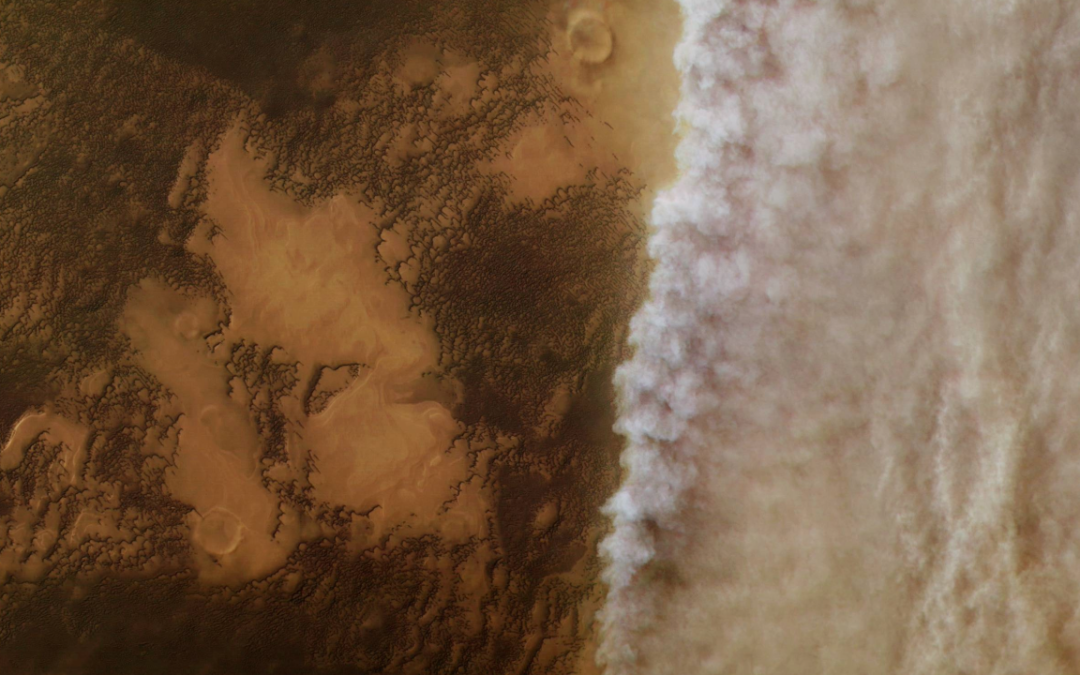
What causes these storms and how do they work differently on the worlds in the solar system. But what about the exoplanets?
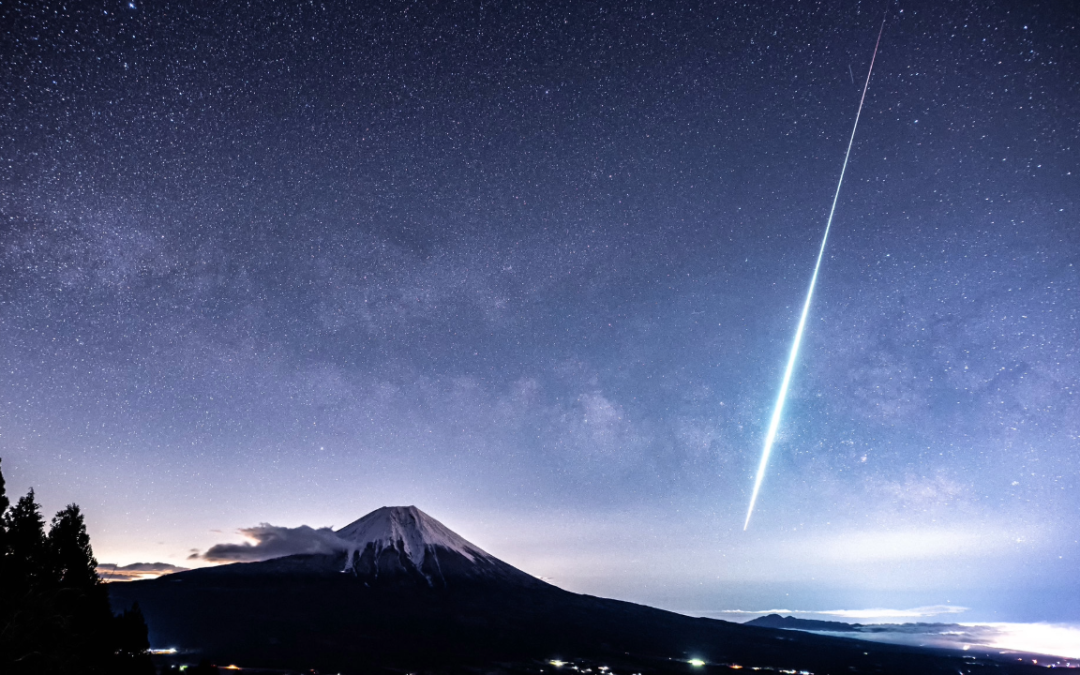

New asteroids are found every day, and every day we learn that those asteroids don’t have any murderous intentions. But how do we learn that?

What time is it on the Moon? The Moon orbits the Earth, so it doesn’t fall into a specific time zone. It’s time to introduce Lunar Time.

Sure, the masses of merging black holes are nice to know, but what else can we learn from gravitational black holes?
Gravity Waves … not gravitational waves … move atmospheres and make pretty clouds.

Pollution will ultimately give away a society.

If you’re an astronomer you depend on accurate observations of stars, but there’s a problem. Stars are sneaky! Changing in size, brightness, color, they hide their chemistry, their age and even their companions from all but the cleverest observers. Stars explode…

From little Ingenuity to the future Firefly and all our Earth Science fliers, let’s look at the buzzy scientists. Soon there’ll be a helicopter flying on Titan, but there are many other flying robots that’ll be helping us with all our science needs.