We are on the verge of sending humans back to the Moon. At the same time others prefer we focus our exploration on Mars. It’s a tough choice.
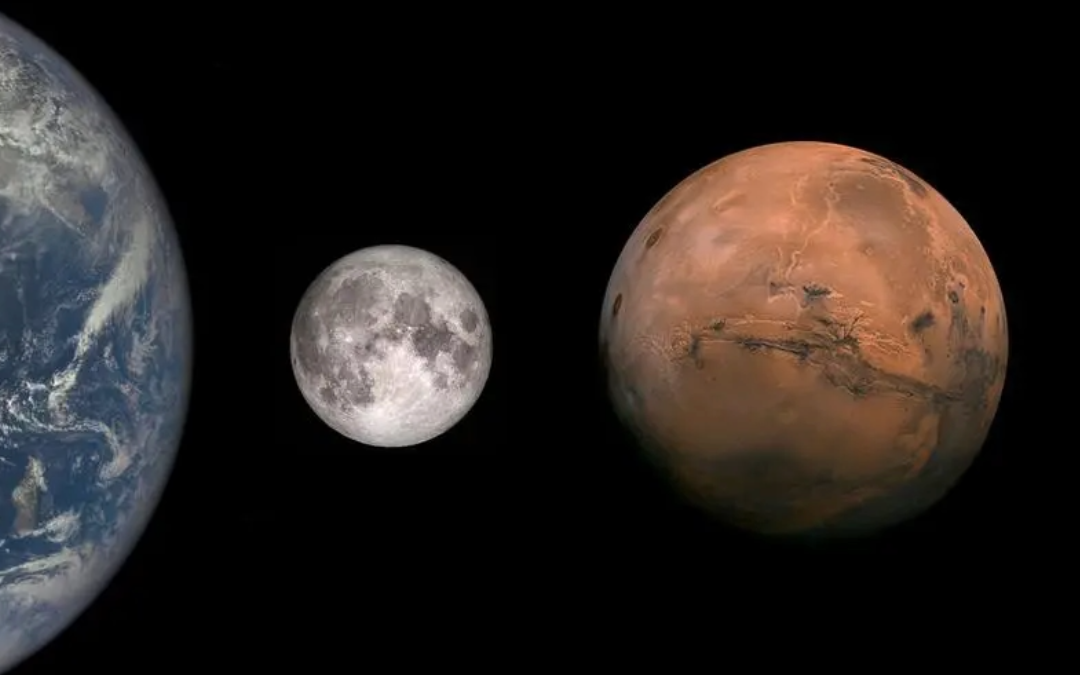


We are on the verge of sending humans back to the Moon. At the same time others prefer we focus our exploration on Mars. It’s a tough choice.

New asteroids are found every day, and every day we learn that those asteroids don’t have any murderous intentions. But how do we learn that?

What time is it on the Moon? The Moon orbits the Earth, so it doesn’t fall into a specific time zone. It’s time to introduce Lunar Time.
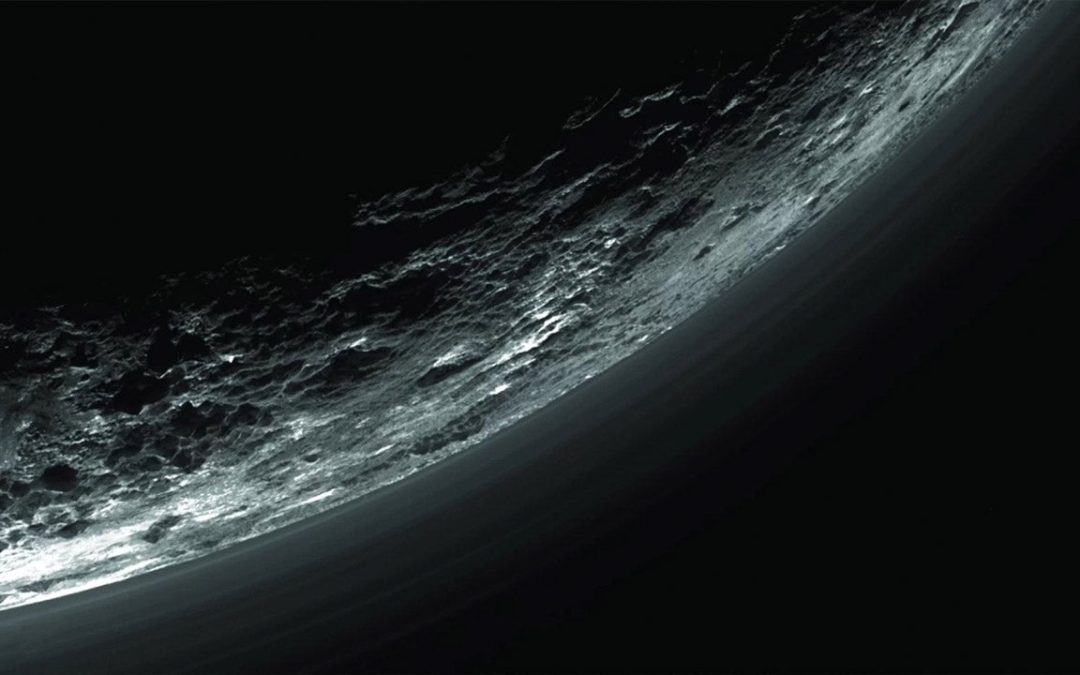
Gravity Waves … not gravitational waves … move atmospheres and make pretty clouds.

2024 was a strange year! But, for space and astronomy we had some interesting, revolutionary, unsettling and downright weird stories pop up. Today let’s talk about them.
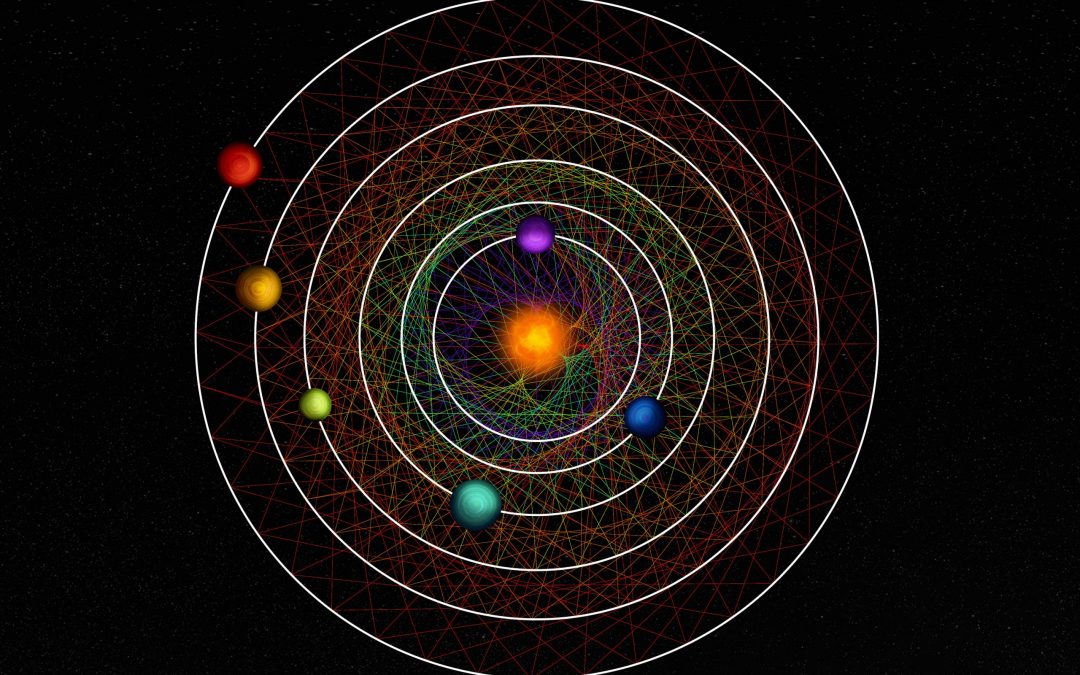
Several of the planets and moons in the Solar System are in orbital resonance, orbiting in a geometric lockstep. And not just the Solar System, astronomers have found the same resonances in other star systems.
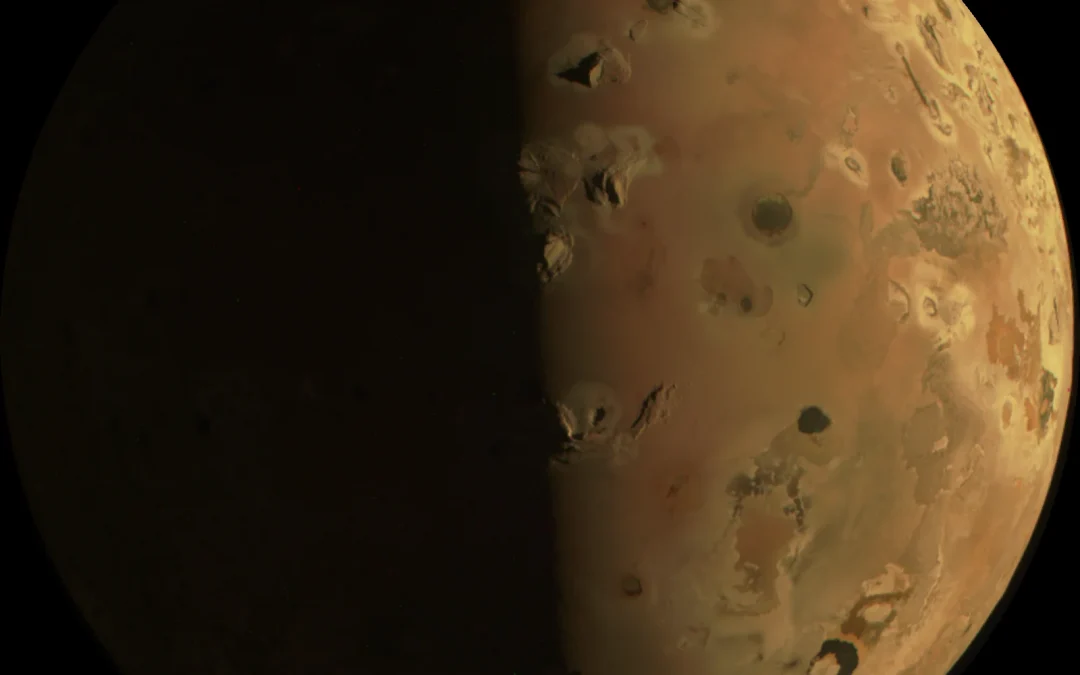
Last week was one of the most exciting meetings we’ve seen from the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, with hundreds of announcements and discoveries from various missions. One theme kept coming up, the Solar System is more volcanically active than we thought. Today, we’ll explore volcanism on other worlds.
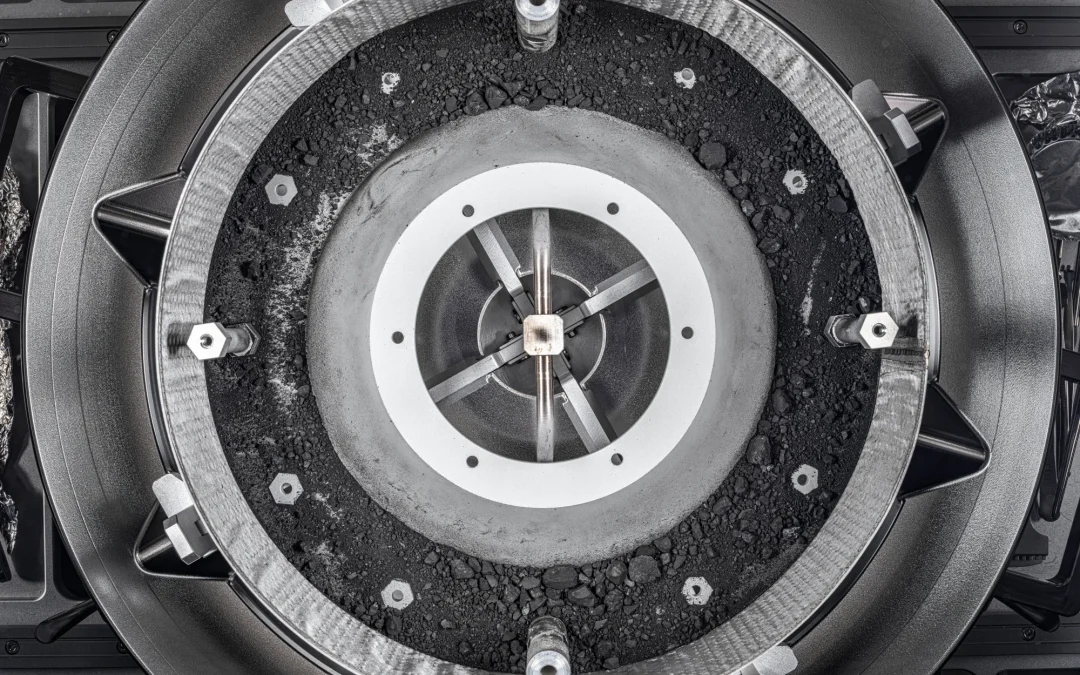

Last week we talked about sample return missions from the Moon and Mars, but scientists have retrieved samples from other objects in the Solar System, including comets and asteroids. What does it take to return a piece of rock from space, and what have we learned so far?

We’ve sent robots to other worlds, but the amount of science we can deploy to another planet can’t compare with the vast science labs we have on Earth. That’s why more and more missions are for a sample return, bringing pieces of alien worlds back to Earth, were we study them with proper equipment.
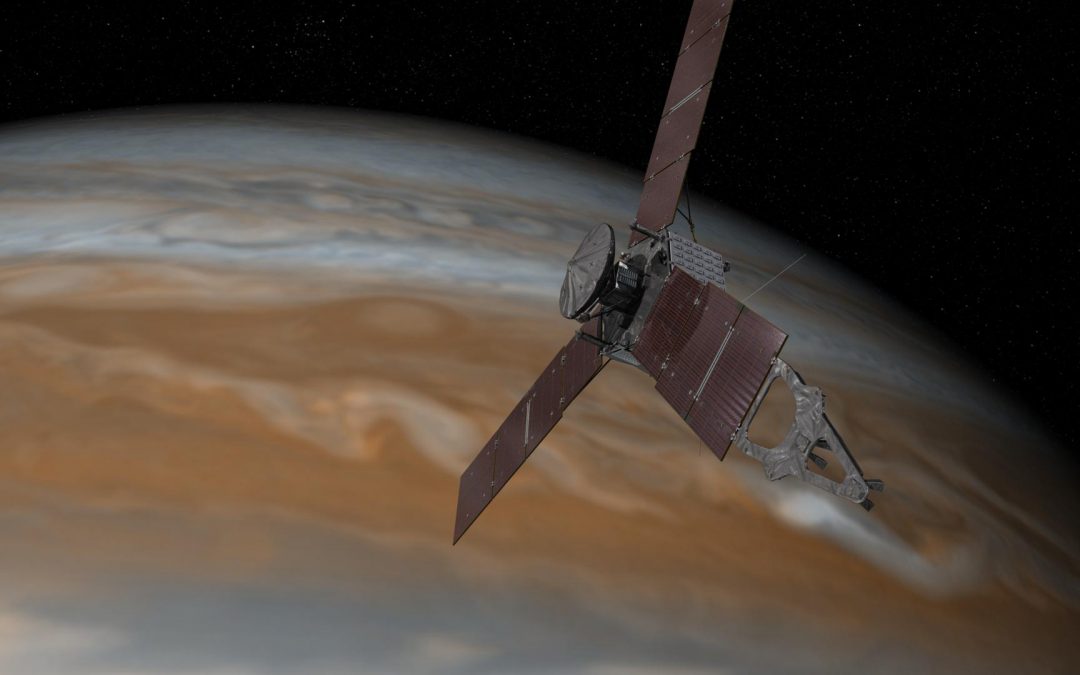

NASA’s Juno spacecraft has completed dozens of flybys of Jupiter, seeing the planet from many angles and delivering some of the most beautiful images we’ve ever seen of the Jovian world. Now it’s focusing in on Io, sending home images of the tiny volcanic world from just 1,500 km away. And the best is yet to come.
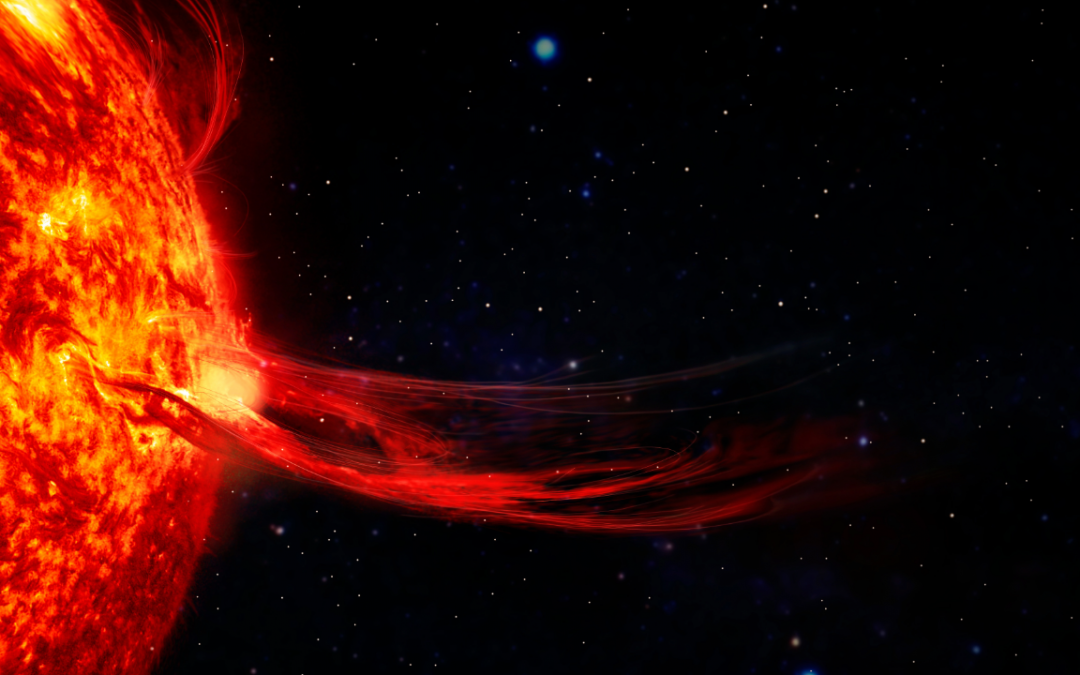

Solar cycle 25 is shaping up to be a doozy, with plenty of flares and coronal mass ejections blasting off the Sun. As the solar activity continues to rise, how are things shaping up?

Finally, we reach the end of our tour through the missions in the Solar System. Out beyond Mars, to Jupiter the Kuiper Belt and Beyond. Recorded live during the CosmoQuestX 2023 Hangout-a-Thon.
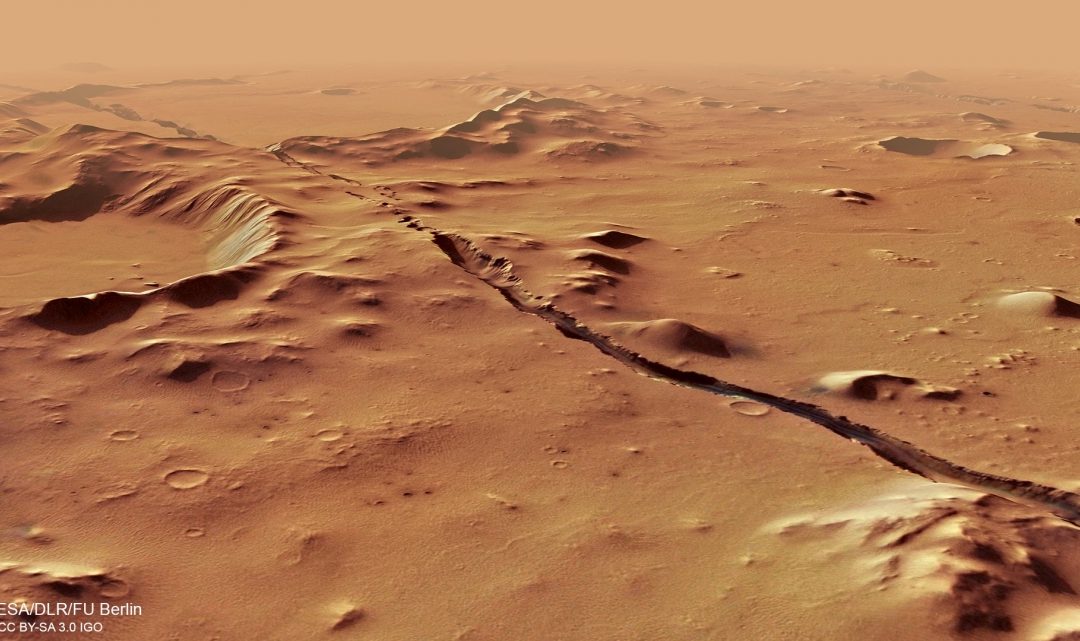
Another week, another review of space missions in the Solar System. Today we set our sights on the red planet. What are all the active missions at Mars today?
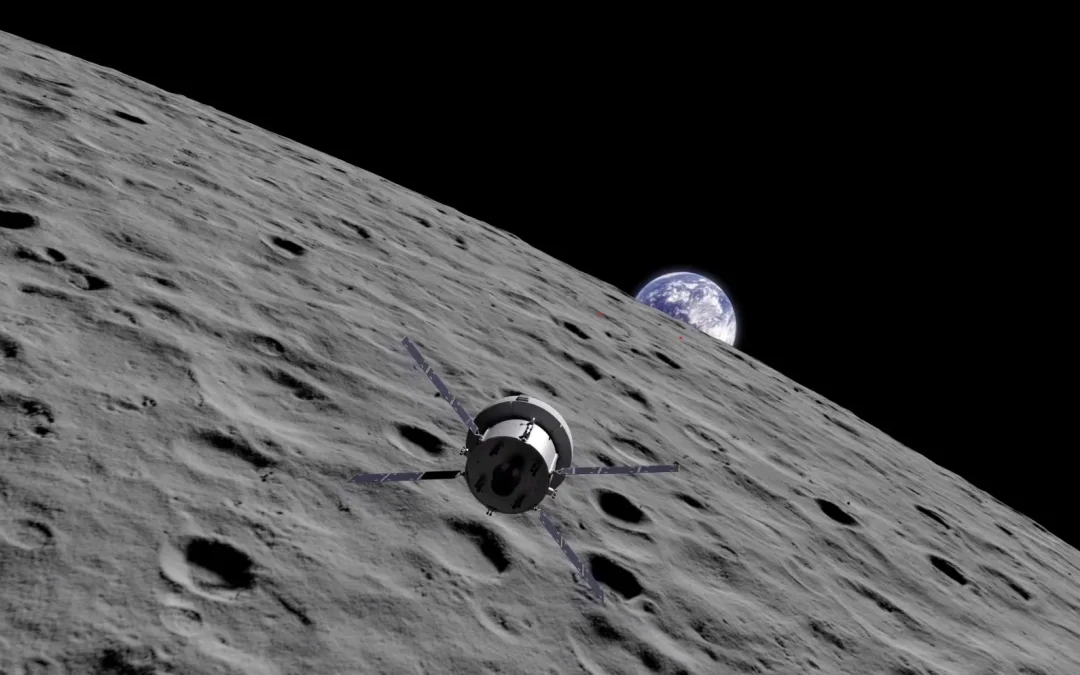

Our journey through missions continues, this time we focus on the Moon. There are many nations on the Moon, near the Moon, around the Moon, travelling to the Moon. It’s a lot. We’ll talk about it today.
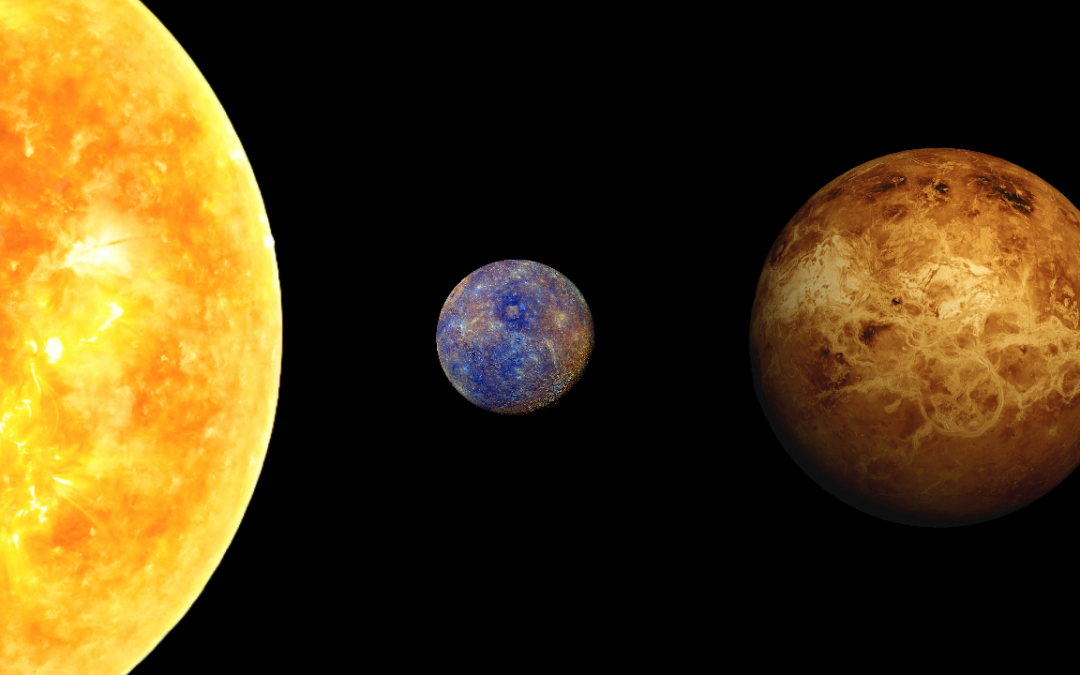
Our journey through space missions continues. Now we move away from the Earth to the rest of the solar system. What’s out there orbiting, roving and flying on other worlds and in interplanetary space. Today we look inward and we’ll talk about the missions studying the Sun, Mercury and Venus.
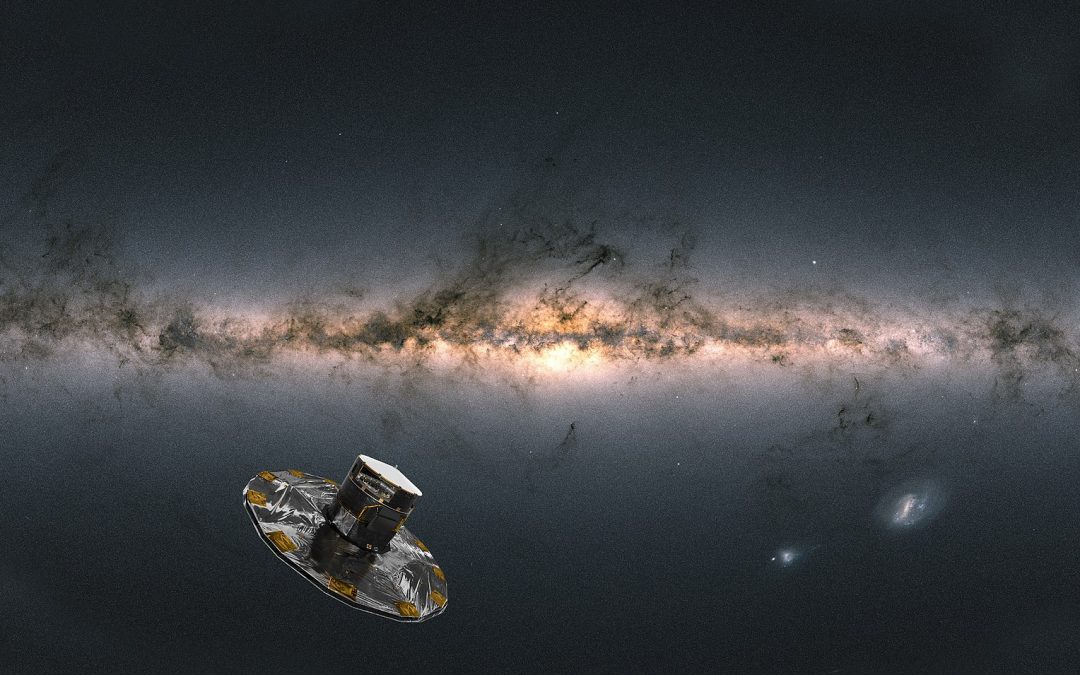

Last week, we brought you up to speed on the spacecraft which are helping to study Earth from above. Many of our missions are in Earth orbit but looking outward to study the Universe. Today, we’ll talk about the missions close to home, helping us understand our place in the cosmos.
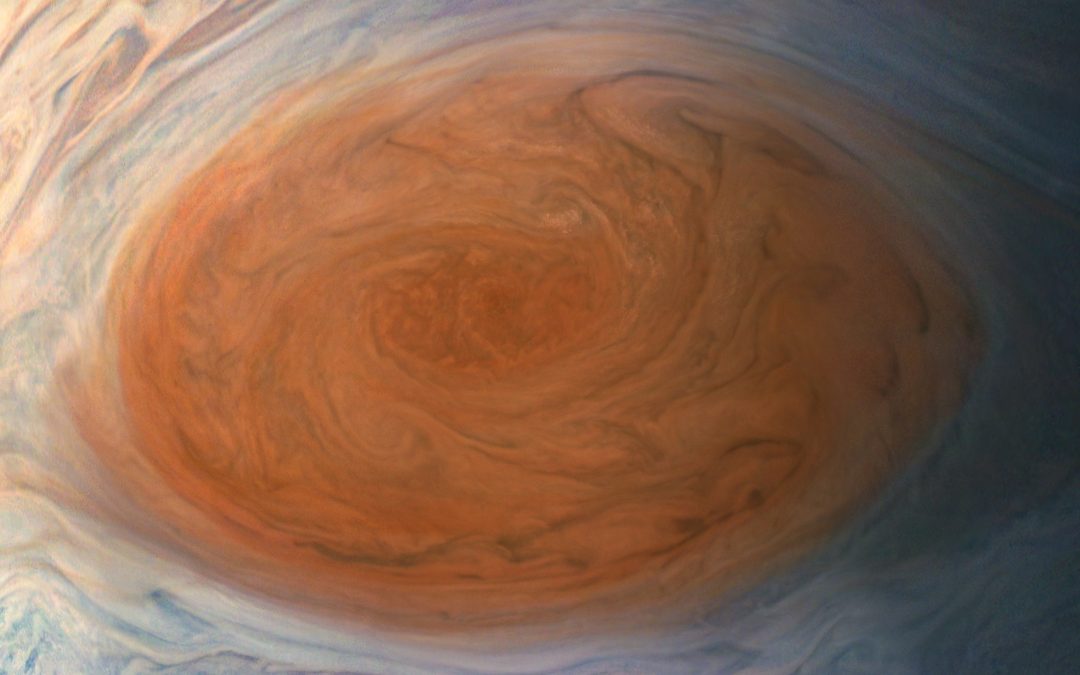

Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is one of its most iconic features, first seen hundreds of years ago. Although it’s certainly long-lasting, it’s been changing in size over the last few decades, shrinking and changing in color. Is it fading away? And what can the changes tell us about storms on giant planets?
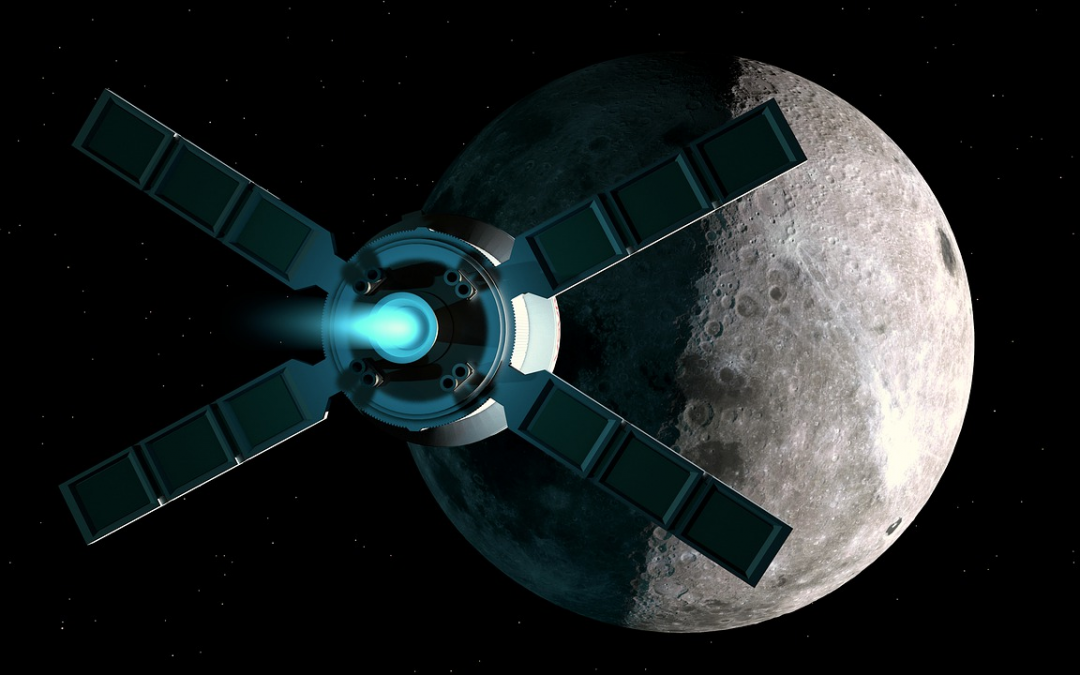
We’re going back to the Moon. In the next few years humans will set foot on the Moon again, ideally this time to stay. But this will be different than the Apollo era, going to the scientifically fascinating, and difficult southern pole of the Moon. What needs to be done to prepare the way back to the Moon?
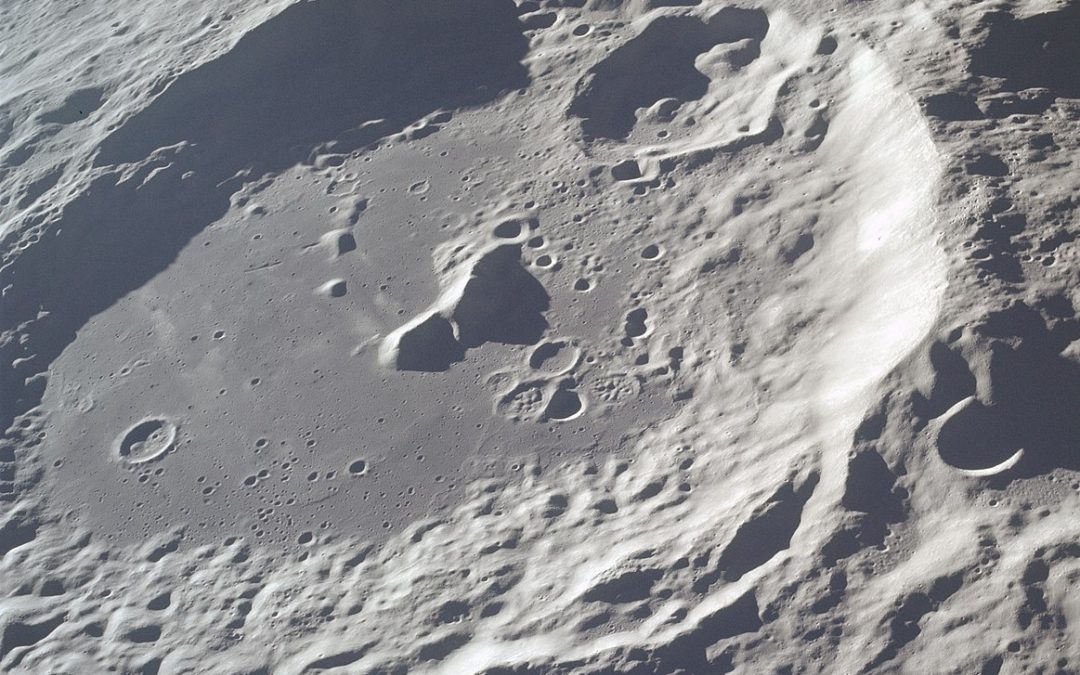

The permanently shadowed craters on the Moon are the focus of so much research. That’s because they seem to contain vast reserves of water ice. Water we could use for oxygen, propellant and so much more, but also, to help us understand where the Earth’s water came from.
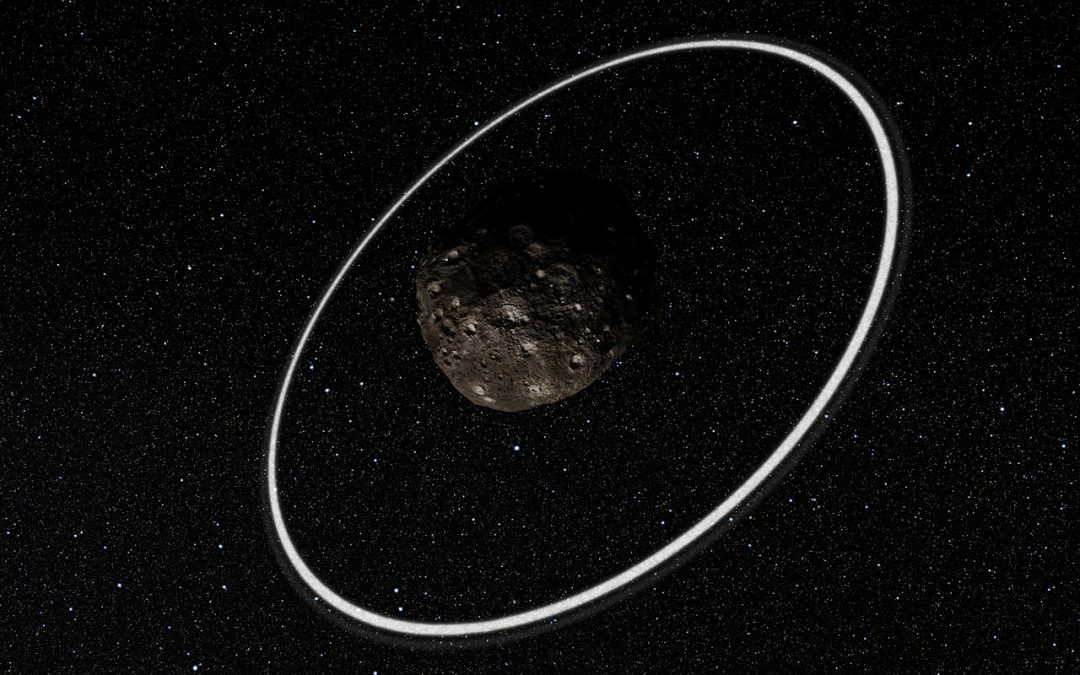

We’ve spent a lot of time gushing about Saturn’s rings, but there are other places with ring systems. And not just Jupiter and the ice giants, but asteroids, dwarf planets, centaurs and even exoplanets. Today we’ll gush about them.

Ice is ice, right? You know, what you get when water freezes. Well, maybe here on Earth. But across the Universe, water can be squeezed together at different temperatures and pressures, leading to very different structures. Today we’ll talk about the different forms that ice can take.
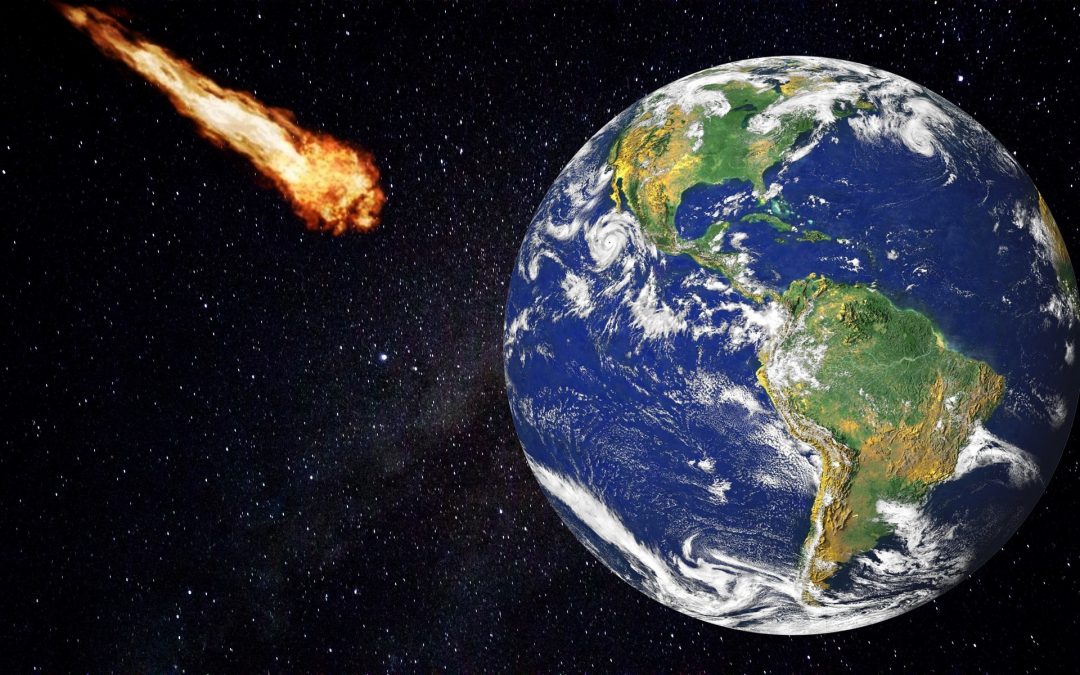

The asteroid apocalypse is one of those existential crises that keep astronomers up at night. But the DART mission showed us that we can push an asteroid off its trajectory if we have enough warning. Today we’ll talk about how humanity is building early warning systems to give us time to respond to a dangerous asteroid.
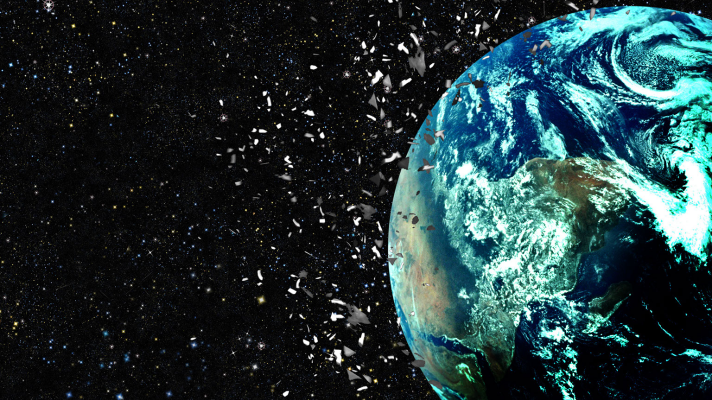

We’ve talked about the rising problem of space junk. Okay, we know it’s an issue. So what can be done about it? Today we’ll talk about ideas to remove space junk, making sure space is open to use for the centuries to come.
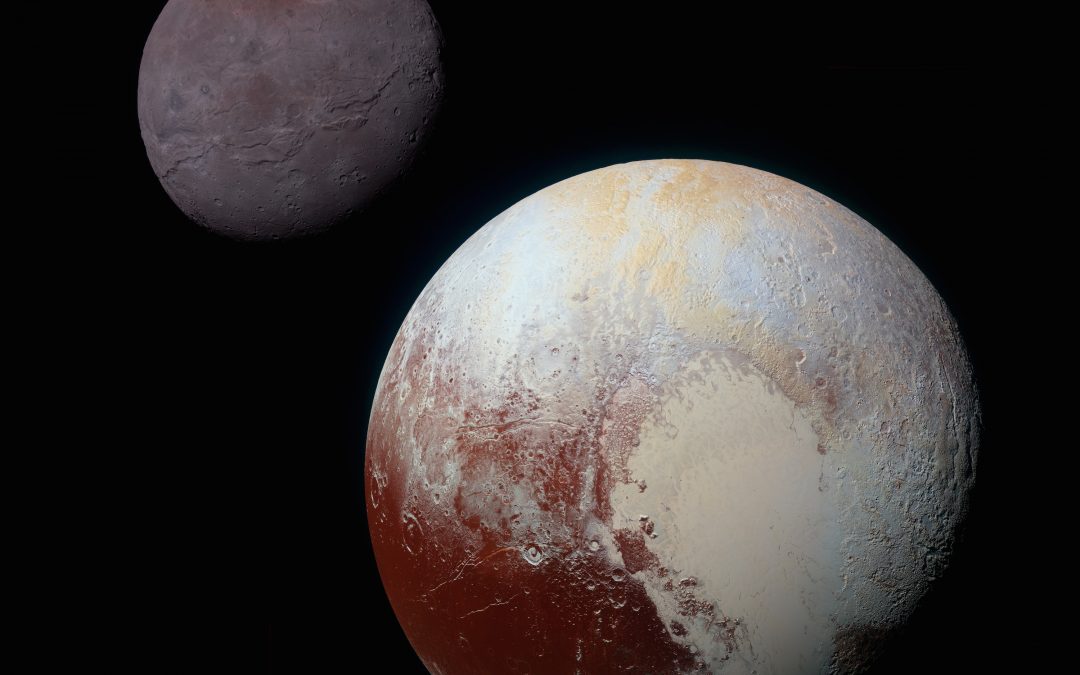

Well, we did it. We made it to episode 666, an auspicious number to be sure. What can we do to celebrate this accomplishment? An episode all about things in the Universe that have been named after mythological people and places in the underworld?
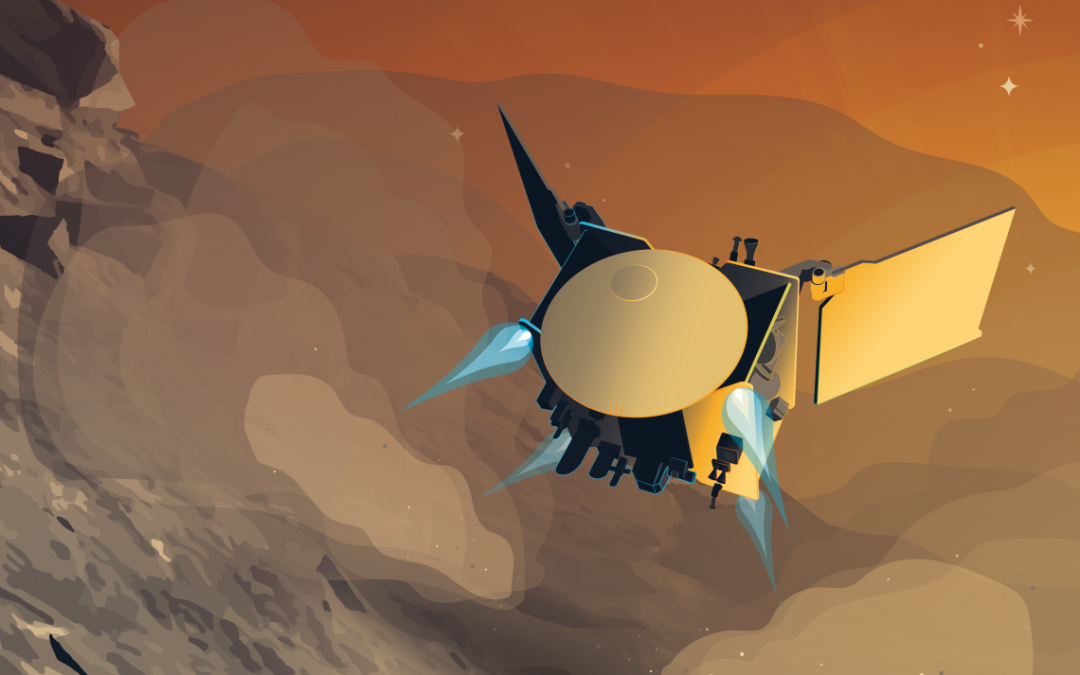

Last week we talked about the missions we’re saying goodbye to. This week, we’re going to talk about some upcoming missions to say hello to. Some are brand new ideas, others are, uh, recycled.